Everything About Tinnitus – Types, Causes, Symptoms, Prevention, Treatments & Latest Researches.
Table of Contents


It was a quiet Sunday afternoon, and I was sitting on the couch while reading a book. My husband and kids had gone out for groceries, so the house was awkwardly quiet,” said Megha (name changed for anonymity).
“I was lost in my thoughts when I started hearing something. It began as a faint ringing noise inside my head, but in a matter of a few seconds, it became loud and clear.”
And here she paused for a moment, “Strangely, now it felt as if the source of the noise was right inside my right ear,” she added.
“Over the next few months, I experienced it numerous times until I finally decided to figure out, what’s wrong with my ear?”
“Since I knew about Dr. Prabha from my cousin, I decided to visit your clinic,” she told us with a smile on her face.
We performed some essential ear examinations followed by a series of audiological tests.
When the reports arrived, she was diagnosed with Subjective Tinnitus. The tests also revealed that she had a mild hearing loss in her right ear, which plausibly triggered the problem.
It was around the summer of 2015 when Megha first visited our clinic, and since then, we have been helping her have an excellent quality of life while managing to keep her hearing loss and tinnitus problem at bay.
After listening to Megha’s story, you might be thinking – What is this strange problem?
Let’s dig into the next section to find out just that.
What is Tinnitus?
Tinnitus (commonly pronounced as TIH-NITE-US or TIN-IH-TUS) in medical terms is described as a non-auditory, internal sound that can be intermittent or incessant. It can happen simultaneously in one or both ears. The sounds can be high pitched or low pitched and can also vary in loudness.
The term Tinnitus comes from the Latin word tinnire, meaning to ring. This problem is commonly described as the ringing in the ears, is the sensation of hearing ringing, buzzing, hissing, chirping, whistling, screeching, clicking, static, roaring, pulsing, whooshing, or musical sounds. Any type of weird noise that you know for sure isn’t coming from an external source.
Typically, people who suffer from this vexing experience these sounds in the absence of outside sounds. However, sometimes it also occurs in the presence of other environmental sounds.
Some Basic Research Data About Tinnitus
According to Medscape, 10-15% of the population of the world suffers from Tinnitus. That is approximately 30 to 40 million people in the USA and more than 190 million people in India.
It is more common in people above 55 years of age and is deeply associated with hearing loss, propounds a Harvard Health Publishing article. For patients already suffering from mild to profound hearing loss or other ear-related symptoms, this number has been reported to be around 85%. This means that 85% of the people with hearing issues suffer from some degree of this ringing problem in the ears.
Development of tinnitus increases in incidence with age. However, in some researches, the rate of ringing in children has been reported as high as 13%, indicating that this issue can occur in people of all age groups.
From our primary research data at Quality Hearing Care, we have recorded over 70% of our mild to profound hearing loss patients complaining of ringing or buzzing in the ears from a survey of over 1800 patients from April 2016.
The next question that comes to mind is – How Does Tinnitus occur? To understand this, we need first to understand…
How Does sound work in our ears?
Hearing seems like a simple and obvious thing that our ears are made to do. But it is when we try to find out how it works that we realize it is an immensely complex process administered by highly sophisticated machinery that has been designed by nature and perfected by evolution.
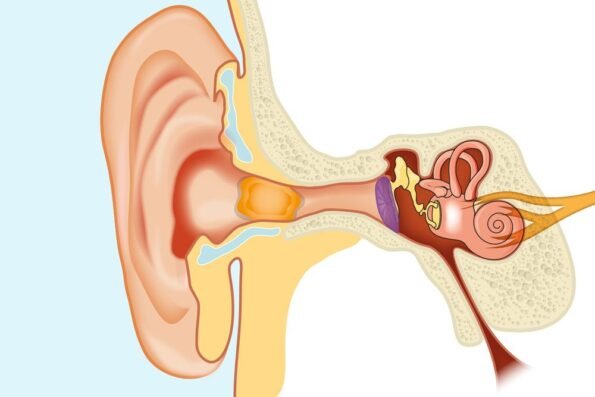
The sound waves of different frequencies emitted from all external sources are first captured by your auricle or what’s commonly known as the Pinna. The pinna shaped like a flattened megaphone with curled up pathways inside it is the visible portion of the outer ear. It plays a vital role in accumulating the sound waves from our environment and channelizing them into the ear canal or scientifically known as the external auditory meatus.
The sound waves then reach a delicate and supple, oval-shaped membrane at the end of the ear canal called the eardrum, or tympanic membrane.
Right behind the eardrum, there is a bijou mechanical apparatus made of bone tissue consisting of 3 very sensitive bones, namely Malleus, Incus, and Stapes. These bones perform a very crucial task of amplifying the sound vibrations and transferring them to the Cochlea.
The cochlea, which is shaped like a snail, is filled with fluid. The sound vibrations make this fluid ripple, which creates waves. Hair like Stereocilia structure sits on top of the hair cell and moves together as hair cell bundles inside the cochlea.
These are responsible for converting the sound vibrations into electrical signals carried to the brain’s auditory cortex by neurotransmitters traveling via auditory nerves.
And voila!! Just like that, we hear a pop.
Whether it’s the sound of a pin dropping or a finger snap or a blaring array of concert speakers, they are all processed the same way. This highly sophisticated machinery performs the same task millions of times non-stop and tirelessly.
There is a beautifully animated video depicting this process by the American National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (NIDOCD) that you can watch below.
So, now that we’ve learned how to pick up a sound. How does that link up with tinnitus?
Let’s find out.
Here’s The Phenomenon That Takes Place In Your Ears Causing Tinnitus
Like every complex machinery, our auditory system is also susceptible to temporary break downs or permanent damage. This damage can happen anywhere along the auditory pathway, from the outer ear through the middle and inner ear to the brain’s auditory cortex, where it’s thought to be imprinted.
The damaged part might start malfunctioning, and as a result, the auditory cortex in the brain does not receive the signals as it was expecting. The brain, in effect, “turns up the gain” on those pathways to detect the signal — in much the same way that we turn up the volume on the radio when we’re trying to find an FM channel’s signal. The resulting electrical noise takes the form of tinnitus.
Injury to the hair cells in the cochlea is one of the most common causes of this ringing issue in the ears. For example, when a loud noise or ototoxic drugs disrupt hair cells, the brain’s circuits don’t receive the signals they anticipate. This stimulates the neurons to have irregular behavior, resulting in the sound or the ringing/buzzing illusion.
Most tinnitus is “sensorineural,” which means it’s due to hearing loss at the cochlea or cochlear nerve level. But this issue may originate in other locations. Our bodies naturally make sounds (called somatic sounds) that we don’t hear when we listen to external sounds. Somatic sounds can be brought to our notice by something that blocks natural hearing. You can get head noise, for instance, when you close your ears very tightly with your hands.
In cases when tinnitus is linked with hearing loss, the patients hear— a high-pitched sound if hearing loss is in the high-frequency range and a low-pitched sound if it’s in the low-frequency range.
Many people experience temporary ringing or buzzing in the ears after exposure to shockingly loud noise such as that of a bomb blast. This type of tinnitus lasts anywhere between a few minutes to a couple of hours.
So how do we keep our ears away from ever experiencing the sound of tinnitus? To do that, we first need to be aware of what causes it. In the next section, we will dive into all the causes of this pervasive issue.
Causes of Tinnitus
Remember how our ears process the sound signals, and the brain interprets the signals sent in the form of neurotransmitters? Our hearing mechanism relies on delicate machinery, and everything that fiddles with this system’s balance can lead to triggering this aberration in your ears.
Let us understand all known causes of this problem in detail below:
1. Tinnitus Due To Hearing Loss:
In most cases, hearing loss happens due to damaged hair cells inside the cochlea. This leads to suboptimal functioning of the cochlea, which results in weaker or random or no signals going out to the auditory cortex. The brain tries to over-compensate for this situation and actively seek out the signals from the cochlea. This leads to the sensation of the made-up sounds in our ears that we know as Tinnitus. The hair cells inside the cochlea can get bent or broken naturally due to aging. Prolonged exposure to loud noise above 100 dB is one of the critical reasons behind damaged cochlear hair cells amongst young people.
2. Tinnitus Due To Ear Canal Blockage due to Ear Wax or Ear Infection:
Any kind of blockage in the ear canal leads to a change in the pressure levels inside the ear. This change in pressure interferes with our hearing mechanism triggering tinnitus. There could be several reasons for blockages. Let’s study them in brief below –
a. Earwax build-up – The hairs inside our ear canal are naturally designed to clean up excess earwax. This is the reason why we often find ENT specialists and audiologists inveighing against the use of earbuds. Since our ears have a natural cleaning mechanism, the use of earbuds does more harm than good. However, in some cases, due to excess dirt or dead skin cells getting deposited inside the ear canal, this process of natural cleaning gets hampered, leading to excess ear wax build-up.
b. Ear Infections – Ear infections lead to the development of pus inside the ear canal. This infection can get triggered due to an injury or dirt or water retention inside the ear. The pus accumulates inside the ear canal to block the pathways of sound waves giving rise to this issue. Here’s in detail about middle ear infections.
3. Tinnitus Due To Head Or Neck Injury:
A severe impact on the head or neck due to an accident can cause damage to the part of our nervous system responsible for carrying sound signals to the brain or the bones and tissues inside our ear or to our auditory cortex itself. Such trauma can lead to malfunctioning of our hearing mechanism, prompting the ringing in the ears. This usually happens in one ear only.
4. Tinnitus Due To Medications:
Tinnitus can come in uninvited as a side-effect of some medicines, especially with a heavier dose. Those who were already battling with this issue may find it worsening due to the consumption of such medications. In most cases, the ringing as a side-effect of medicines vanishes with the termination of these drug doses. Some of the common medications that are scientifically recognized to cause tinnitus are Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs), Water Pills (Diuretics), Antidepressants, some Antibiotics, Aspirin (very high doses of it), some Chemotherapy medicines, and other Cancer Drugs.
5. Tinnitus Due To Anemia:
Anemia is a health condition caused by the deficiency of healthy red blood cells in the blood. This lack of red blood cells or dysfunctional red blood cells can sometimes cause the blood to thin and flow swiftly through the body, producing some internal sounds.
6. Tinnitus Due To Meniere’s Disease:

Meniere’s disease is an ear disorder caused by the abnormal pressure of the inner ear fluid. This can lead to hearing loss or even vertigo. This the lesser known relations between tinnitus and vertigo. Tinnitus can be an early indicator of Meniere’s disease. If your reason is not mentioned in this list, you might want to consider getting yourself checked for Meniere’s disease by an ENT specialist doctor.
7. Tinnitus Due To Muscle Spasms In The Inner Ear:
Neurological diseases such as Multiple Sclerosis can cause the inner ear muscles to tense up (spasm), leading to hearing loss and tinnitus. The muscle spasm can sometimes happen on its own for no explicable reasons.
8. Tinnitus Due To Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
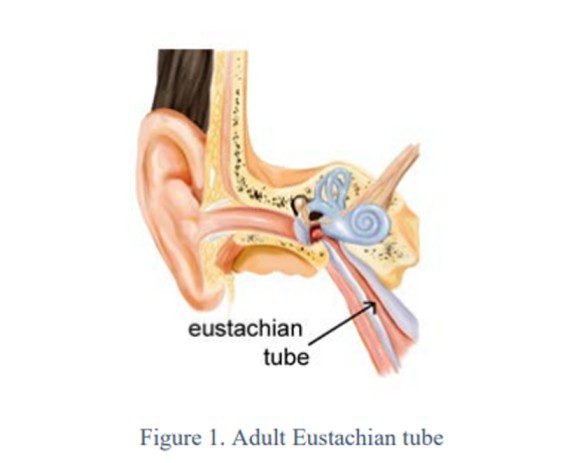
The eustachian tube connects our middle ear to the upper throat. The dysfunctioning of this tube leads to its expansion, making the ear feel full all the time. Such a feeling inside the ear can also prompt this issue.
9. Tinnitus Due To Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Disorders:
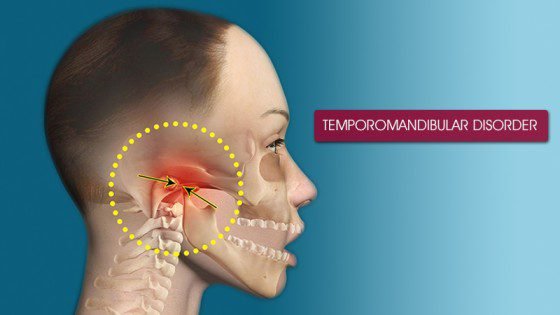
The joint on each side of our head where the lower jawbone meets the skull is called the temporomandibular joint. Besides being anatomically close to the ear, it also shares some muscles and nerves with the middle ear. These multiple connection problems with the muscles, cartilage, and ligaments of the TMJ can also impact the ear leading to the buzzing in your ears.
10. Tinnitus Due To Changes in Ear Bones:
The ear bones grow abnormally in some people leading to stiffness around the middle ear. This condition is scientifically known as Otosclerosis. It can be genetic. The stiffness caused by abnormal bone growth may affect hearing and trigger tinnitus.
11. Tinnitus Due To Perforated Eardrum Or Eardrum Rupture:
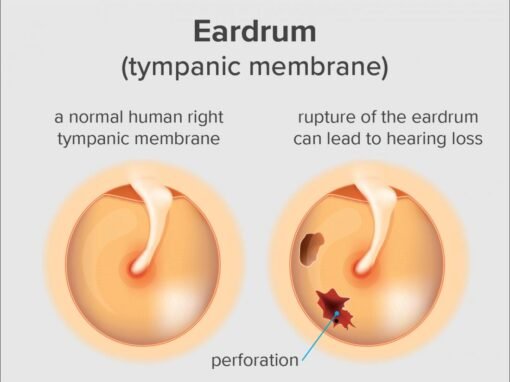
The leading cause of damage to the eardrum is a booming sound like an explosion or jet propulsion engine. It’s beyond the capacity of our eardrums to vibrate with such high frequency sounds waves. Exposure to such sounds can therefore rupture or perforate the eardrum causing ringing in the ear or hearing loss.
12. Tinnitus Due To Acoustic Neuroma (or other Head and Neck Tumors):
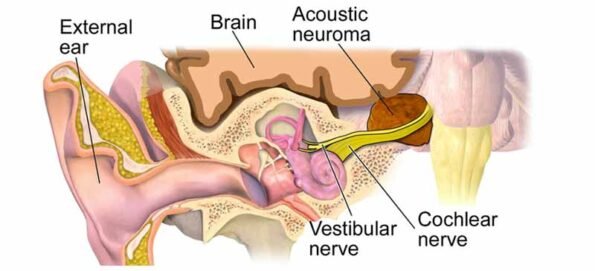
The cranial nerve runs from the brain to our inner ear. It is responsible for controlling our balance and hearing. Acoustic neuroma is a noncancerous (benign) tumor that develops on the cranial nerve. This tumor, however, being non-fatal, can sometimes lead to hearing loss tinnitus.
13. Tinnitus Due To Blood Vessel Issues:
Narrowing of arteries (medically known as Atherosclerosis) or High Blood Pressure, or kinked or malformed blood vessels are conditions that can cause the blood to move with more force through the veins or arteries. These changes in blood flow can cause tinnitus or make the issue more prominent.
14. Tinnitus Due to Thyroid Issues:
Thyroid issues arise from an overactive thyroid gland (medically known as Hyperthyroidism) or an underactive thyroid gland (medically known as Hypothyroidism). Hypothyroidism is known to have an impact on hearing capabilities and can also lead to this problem in your ears. The thyroid gland’s thyroxine hormone is also responsible for the development of our auditory system. The lack of thyroxine can therefore affect our auditory system prompting hearing loss and tinnitus.
Hyperthyroidism leads to an increased heart rate, which can cause damage to the ears triggering hearing loss and the incessant buzzing in your ears.
15. Tinnitus Due To Paget’s Disease:
Paget’s disease is a problem that disrupts the normal cycle of bone tissue repair and renewal. Over time, this can cause the bones to become fragile and misshapen. The bones in our pelvis area, skull, spine, and legs are usually affected by it. When Paget’s disease affects the skull, it can damage the bones or the neural network between the ears and the brain. Paget’s disease of the temporal bone can lead to permanent hearing loss or even complete deafness. According to an article published by Dr. Louis Hofmeyr, 20% of such patients with Paget’s temporal bone disease have been recorded to have tinnitus issues and hearing loss. Tinnitus due to Paget’s disease may be pulsatile.
16. Tinnitus Due To Diabetes And Other Chronic Conditions:
Prolonged high blood sugar levels in the body have been observed to cause damage to the eighth cranial nerve, which is linked to maintaining body balance and our auditory system. Damage to this cranial nerve and lead to hearing loss and tinnitus.
Other chronic conditions and autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus can also trigger this ringing in your ears.
Now that we have learned about various cause of tinnitus, it makes us wonder if all the tinnitus types triggered due to these underlying causes are the same.
Let’s explore in the section of this article.
Types Of Tinnitus
Tinnitus is a common condition faced by millions of people across the globe. But the types of tinnitus that people suffer from might be very different in nature and origin. Everyone’s problem is slightly different, even in terms of the symptoms of tinnitus, especially the kind of sound they hear during an episode.
Let’s try and understand all the different types of tinnitus. If you feel you are also dealing with this issue, then your type of tinnitus will most likely fall within one of these categories. In here, you will also find the answer to the question: can tinnitus be cured?
1. Subjective Tinnitus:
In this type of tinnitus, only the patient can hear the ringing/buzzing sound inside the ear. It is one of the most prevalent kinds of tinnitus primarily caused by exposure to loud noise. It happens intermittently and varies in duration and intensity of the sound.
Subjective tinnitus can often interfere with the actual environmental sound, making it difficult to focus on the essential sounds. It can even prove risky in some situations leading to loss of balance or accidents.
Subjective tinnitus can be treated with certain specialized hearing aids that play a calming noise, distracting the patient from the tinnitus noise. To know more about these hearing aids and consult leading audiologists from India, please visit Quality Hearing Care.
2. Sensory Tinnitus:
Sensory tinnitus is the other most common type of tinnitus. It usually occurs as a concomitant of hearing loss or an impaired auditory system.
There is no perfect cure for sensory tinnitus, but some programs can help manage it better and mitigate the symptoms of tinnitus.
Sensory tinnitus can also be deemed a form of subjective tinnitus linked to how the brain processes sound. Sensory tinnitus is also known as Neurological tinnitus, and it can lead to people feeling off-balance at times.
3. Somatic Tinnitus:
Somatic tinnitus is usually triggered by physical movement or touch, such as muscle spasms around the neck or ear area.
It can also arise from dental issues such as wisdom teeth and jaw popping. Since somatic tinnitus is caused by all outside factors, rather than neurological factors, it is also known as conductive tinnitus.
Sound therapy and massage therapy are highly effective treatment for tinnitus that help manage this form of tinnitus.
4. Objective Tinnitus:
Objective tinnitus is considered one of the rarest by medical practitioners, but it often has an identifiable cause and may be curable.
Your doctor or audiologist can even hear this type of tinnitus with the help of a stethoscope. So in the case of objective tinnitus, your auditory cortex is not making up the sound to fill in for your lack of hearing ability, but there is a natural sound in this case.
Vascular noises or Eustachian tube dysfunction, or muscular contraction of palatal or middle ear muscles may be the underlying cause of this type. In some cases, the sound of objective tinnitus appears in sync with the heartbeat.
If you know someone suffering from this problem and then you might have thought about – How serious can this problem get? Read on to discover.
Is Tinnitus An Acute Medical Problem – How Serious Can It Get?
Tinnitus comes and goes for some people without really affecting their life, but it may significantly impact others’ quality of life.
This problem can sometimes lead to increased stress, depleted concentration, anxiety, insomnia, and even depression. These could be some of the most intense side-effects of this issue. Let’s study some of the common ones in detail below:
1. Tinnitus And Stress:
Tinnitus has been proven to induce stress. The level of stress could vary from person to person and also on the intensity of the ringing. Below are some of the tips that can help in dealing with stress due to tinnitus :
a. Accepting the issue and staying calm about it. Try not to get agitated about your tinnitus, trust the management process laid out by your doctor and follow it religiously.
b. Try to meditate in a way that helps you relax.
c. Think positively – feeling negative can aggravate the problem.
d. Try to habituate your mind to tinnitus. Know that it is not a life-threatening disease, and you don’t need to be stressed about it.
2. Tinnitus And Insomnia:
Everyone’s sleep requirement is different. What matters is that have you obtained enough sleep in the night to feel refreshed and energetic in the morning?
Insomnia is defined as lack of sleep or poor quality of sleep followed by daytime fatigue. Almost 50% of the people who experience acute levels of tinnitus initially report a disturbance in their sleep.
The effects of insomnia start to surface only after a week or more of a disturbed sleep cycle. Below are some of the common symptoms of insomnia:
a. Physical tiredness
b. Difficulty in concentrating
c. A feeling of depression and lack of motivation
d. Irritation and Lethargy
Insomnia is primarily triggered by stress that comes along with this issue. Presence of other comorbidities such as – arthritis, migraine, asthma, or psychological factors such as – emotional crisis, depression or drug or alcohol abuse, or sleeping medication combined with tinnitus can trigger insomnia or make it even worse.
To combat insomnia caused by the ringing in your ears, it’s vital to look at all the contributing factors before developing a cure. Relaxation techniques, such as yoga, meditation, biofeedback, and progressive relaxation, are known to have significantly improved patients’ conditions.
Wondering what might work well for you or someone you know who is dealing with insomnia and tinnitus? Apart from consulting your doctor, you can always try out some relaxation techniques to discover what works well for you. If you are wondering: can tinnitus be cured naturally, here’s the ways you can try to make it better.
As far as adjusting the sleep cycle is concerned, below are some tips that might come in handy:
a. Wake up at the same time every day. We know it’s possible that you couldn’t sleep all night, and just half an hour before your regular alarm time, you start feeling slumberous. Yes, the rest of the day, you are going to feel like a zombie. But it’s better to spoil one day than an entire week or possibly even months. This one sacrifice of your sleep will help you adjust your sleep cycle and induce sleep at night.
b. Avoid serious discussions or arguments before bedtime.
c. If you don’t fall asleep in half an hour at night, get up and do something that engages your brain, for example – reading, meditation, breathing exercises, etc. You can even prepare a to-do list for the next day or plan a holiday, or do some creative work for which you can’t take time during your work hours. Try to go back to sleep in about 20 minutes, and hopefully, you’ll be able to relax better. The same applies if you wake up in the middle of the night.
d. Avoid eating heavy meals just before bedtime.
e. Reduce consumption of alcohol, chocolate, tea, coffee, soft drinks, cigarettes.
f. Mild, full-body exercise can help you beat stress and fatigue, making it easier to sleep at night.
g. If your comorbidities are contributing to your sleep disturbance, seek immediate advice from a medical practitioner.
In many cases, the ringing/ buzzing subsides gradually, or otherwise, our body gets used to it.
However, it is essential to find the underlying cause of tinnitus and treat it by seeking appropriate medical advice. Early diagnosis and treatment of tinnitus can also help in reversing the condition entirely.
In our next section, let us understand how a medical specialist can help diagnose and manage the issue.
How Can An Audiologist Or ENT Specialist Help In Managing Tinnitus?
This article will help you go prepared to the doctor to explain your problem correctly to the doctor and get the maximum benefit from the visit without wasting time. It is essential to know the following:
1. How to explain your tinnitus issue to your doctor? What may he ask which you need to go prepared with?
It is common practice just to tell our symptoms to the doctor. But in the case of this problem, your doctor would also like to know about how it affects your life. Here’s a list of questions that your doctor may ask, and it is always advisable to go prepared with the answers:
a. What are the most obvious symptoms of tinnitus that you have noticed?
b. Are you having difficulty concentrating or sleeping?
c. Do you feel fatigued?
d. Are you having any relationship issues?
e. Do you have a thyroid imbalance or high blood pressure?
f. Have you had any sudden exposure to thunderous noise such as that of a blast or long-term exposure to loud noises, including at work?
g. Are you taking any medications? You may have to provide full details about it.
h. Have you ever had a neck or head injury?
i. Do you drink alcohol or consume a lot of coffee?
j. Do you smoke?
k. Do you have any emotional or mental stress due to work or relationships?
As you must have noticed, these questions are a mix of your medical and personal history, which is vital for the doctor to understand your case.
It is also crucial for you to know what’s going on in your body, and the medical specialist can help you understand it better. Therefore, you must go prepared with the right questions to ask your doctor.
2. What questions should you ask your doctor about tinnitus?
Having better knowledge about this issue is the key to be able to manage it better. You should ask your doctor the following question to better understand your condition:
a. What type of tinnitus do you have?
b. What is the cause of your problem?
c. Is your type of tinnitus going to affect your mental health?
d. Can the noise coming from your ears be heard by others?
e. Could your tinnitus damage your hearing power?
f. Is your tinnitus a symptom of an underlying hearing loss issue?
g. What are the best possible treatments for tinnitus?
h. What are some home remedies that can be done to manage tinnitus?
i. Does the treatment advised by the doctor have some side-effects? If yes, how can you prepare to mitigate them?
j. What can you do to prevent your tinnitus from getting worse?
Being prepared with these questions and answers will ensure that you can get the maximum benefit from your visit to the doctor. A complete medical diagnosis might still be required.
3. How can tinnitus be diagnosed?
Tinnitus is mostly a subjective condition. However, there are clinical ways to measure its properties and the effects they have on the patient. The first step in managing the ringing in your ears is duly diagnosing it. Below are two primary ways in which the ringing in your ears can be diagnosed:
a. Audiometry Tests:

The hearing care specialist is going to examine your ears and conduct a sound test. A device will transmit sounds through a set of headphones to one ear at a time. You’ll have to respond by raising your hand each time you hear a sound. Your doctor will then compare the sounds you hear against what an average person of your age should identify with any particular frequencies of sounds you have trouble hearing. The audiometric evaluations for tinnitus and hearing loss are generally common. They include:
i. Speech Recognition Test: It is also known as speech audiometry. In this test, the patient is made to hear some words first, and then he or she is asked to repeat them to check if they were able to listen to the words correctly.
ii. Pure Tone Audiogram: This test is used to measure a patient’s ability to hear different frequency sounds at different volumes. A chart is plotted to analyze the results.
iii. Tympanogram: This test is used to measure the mobility of the tympanic membrane and the conduction bones. It is an objective test that measures the functioning of the middle ear.
iv. Acoustic Reflex Testing: This test is used to measure how the muscles in the middle ear contract in response to various sounds. The Acoustic Reflex test is an objective test.
v. Otoacoustic Emission Testing: This test is performed with sensitive microphones to observe how the hair cells move inside the middle ear.
b. Imaging Test:
Your doctor may also advise you to get a CT scan or an MRI to check for any deformity or damage inside your ears. The imaging test could also show light on tumors, blood vessel disorders, or other abnormalities that can affect your hearing.
4. How Do Audiologists Measure The Impact Of Tinnitus?
As described above, the audiologists, hearing care specialists, or ENT specialists deploy many techniques to test tinnitus attributes. Below are some of the essential measurements that they try to analyze to understand the nature of the problem fully:
a. It’s essential for an audiologist to understand the gaps in a patient’s hearing spectrum, as this correlates to the nature of their tinnitus. (For instance, patients with high-frequency hearing loss usually get high-frequency ringing, and low-frequency hearing loss is linked to low-frequency ringing). These markers also help the doctor in devising an appropriate prognosis plan.
b. The hearing care specialists use many tests to measure the patient’s perception of tinnitus like sound, pitch, and volume. When evaluating the cases, hearing health professionals use an additional set of tests.
i. Tinnitus Sound Matching: The hearing care professional presents the patient with different tinnitus sounds, asking them to match it with their tinnitus sound. Sound matching provides an essential baseline for customizing therapies for each patient based on the type of sound they hear.
ii. Minimum Masking Level: Here, the audiologist tries to find out the minimum volume of an external sound that can completely mask the sound of tinnitus. This helps the doctor in understanding how loud is the sound of tinnitus inside a patient’s ear. This allows the doctors to develop effective tinnitus management therapies.
iii. Loudness Discomfort Level: This is an indicator of the volume at which external sound becomes unbearable for a tinnitus patient. This measurement helps the doctor understand the feasibility of sound therapy, masking, and hearing aids as potential treatments.
iv Additional Tests: A hearing health professional may need to make some different measurements for other health factors. This is usually required if the patient has comorbidities.
There are numerous other subjective tests to measure the experience of a patient’s tinnitus. The American Tinnitus Association has a list of free downloadable documents on these that can be referred to for more information. However, one must note that one must still consult a hearing care specialist to seek a proper diagnosis and treatment.
5. Tinnitus – Professional Tinnitus Treatments And Strategies To Manage
Over 70% of the patients we interviewed at Quality Hearing Care assumed that there could be no way to manage the problem. While this appears to be the common perception of the people, it’s not correct. The fact is that there are numerous management techniques that hearing care professionals can recommend to mitigate the effects of this aberration in your ears. Below are some of the effective methods that are used by hearing care professionals:
a. Hearing Aids:

In most cases reported by medical practitioners, this issue is observed as a symptom of a mild to profound hearing loss. Therefore, using a hearing aid in such cases is an effective way to manage both problems. A hearing aid is a small electronic device that usually rests behind the ear with a microphone, amplifier, and speaker that delivers the sound inside the ear canal after increasing the volume of external noises. Hearing aids come in different shapes, sizes and prices. If you wish to know all about different types of hearing aids, you can follow the hyperlink. If you would like to know what should be the ideal process to follow while researching and buying a hearing aid, you can check out this unique 7 step process for first-time hearing aid users. If your tinnitus is linked to hearing loss, the better you hear, the lesser you feel the effects. In 2007, The Hearing Review published a survey of hearing care professionals where they found that 60 percent of their patients with tinnitus were relieved up to some extent by the hearing aid. 22% of the patients experienced significant relief.
b. Tinnitus Retraining Therapy:
This therapy is primarily aimed at habituating the brain about tinnitus. It uses a mix of counseling and sound therapy to train a patient’s mind not to be bothered by tinnitus. Various researches conducted across the world peg the success rate of this therapy anywhere above 80%. You can refer to this Audiology Online article for a more detailed account of this therapy and the studies conducted around it.
c. Sound-masking devices:
Sound-masking devices are used to deliver a pleasant or benign external noise that masks or covers tinnitus’s internal sound. There are various types of sound masking devices available. Some are tabletop sound machines, while others can even fit inside the ear canal. These devices play white noise, pink noise, nature noises, music, or other ambient sounds. You can adjust the volume setting on these devices just to distract you from the ringing sound in your ear or completely overpower it. They can also be used to relax and fall asleep.
A study conducted by Frontiers In Aging Neuroscience in 2017 found that white noise or pink noise was much more effective in curbing the ringing sound in your ear than the sounds of nature, which were much less effective.
d. Modified or Customized Sound Machines:
The sound masking devices, as explained above, are only effective while a patient is using them. They do not have any long-lasting effect. On the other hand, the modified sound machines deliver customized sounds explicitly tailored as per a patient’s tinnitus. These machines have to be worn only for a fixed amount of time, but the patients can experience its benefits even long after the device is turned off. Over time, the patient experiences a permanent improvement in the perceived loudness of their ringing.
In 2017 a study was published in the Annals of Ontology, Rhinology, and Laryngology about how customized sounds do a better job of curbing the tinnitus sound than broadband noises.
e. Acoustic Neural Stimulation:
Acoustic Neural Simulation is mainly used for very loud and persistent tinnitus. It uses a device that embeds some acoustic signals in music and delivers it to the ears via headphones. These acoustic signals help stimulate a change in the brain’s neural circuits, making it less sensitive to tinnitus. Various trials conducted by medical researchers around the globe are seeing promising results coming from this therapy.
f. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy:
Tinnitus could lead to a high level of stress, which sometimes triggers depression, anxiety, and insomnia. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) does not help reduce tinnitus’s sound but allows the patient to learn to live with it. The goal of CBT is to mitigate the effects of this problem on your mental health.
CBT involves weekly sessions with a therapist or counselor to identify and change negative thought patterns. A study published in the Korean Journal of Audiology has found cognitive behavioral therapy to curb the psychological effects of this problem effectively.
g. Cochlear Implants:
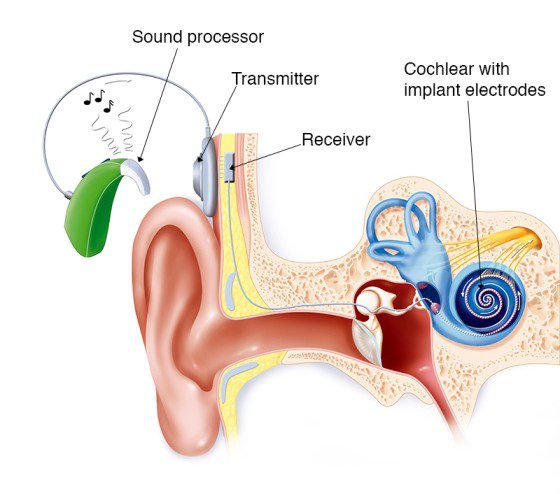
Cochlear implants are used to replace and bypass the damaged part of the inner ear. These implants are often advised for patients with severe or profound hearing loss. The implants process the sound captured by the pinna and convert it directly into electrical signals that are delivered to the auditory nerve. This treatment is used in severe or profound hearing loss cases where hearing loss is the root cause of tinnitus. Therefore, the cochlear implants don’t treat the ringing but rather the underlying hearing loss triggering it.
h. Progressive Tinnitus Management:
Progressive tinnitus Management (PTM) is a treatment program offered by the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs. The armed forces personnel are often exposed to loud noises during their service. This exposure to loud noise often leads to noise-induced hearing loss that can lead to tinnitus.
i. Antidepressants and Antianxiety Drugs:
In combination with other therapies, your doctor may prescribe some medicines to make your symptoms less annoying. Antianxiety drugs are prescribed to those who are also dealing with insomnia due to tinnitus. Alprazolam (Xanax) is known to provide some relief from anxiety to tinnitus patients.
Some of the commonly used antidepressants for tinnitus patients include:
i. Clomipramine (Anafranil)
ii. Desipramine (Norpramin)
iii. Imipramine (Tofranil)
iv. Nortriptyline (Pamelor)
v. Protriptyline (Vivactil)
j. Treating Dysfunctions and Obstructions:
Suppose the ringing in your ears arises from any kind of obstruction or dysfunctioning of other parts of the body around the auditory system, such as a problem with the Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) or excess earwax. Then a suitable medical procedure may have to be performed to clear such obstructions. These obstructions and dysfunctions can be of many types, and therefore it’s best to take the advice of your ENT specialists for the same.
k. Exercise:
Exercise can help reduce the stress caused due to the disturbance in your ears. This ensures that this problem does not lead to other psychological or mental health issues. It’s more of a preventive or a general well-being treatment.
l. Mindfulness-based Stress Reduction:
Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR) meditative training program designed to draw the patient’s attention away from the ringing or the buzzing sound. A study published in The Hearing Journal found that participants of an eight-week MBSR program experienced significantly altered tinnitus perceptions. This included a reduction in depression and anxiety.
m. Alternative Treatments:
Some other alternative treatments sometimes suggested by hearing health professional include:
i. Nutritional Supplements
ii. Homeopathy
iii. Acupuncture or Acupressure
iv. Hypnosis Therapy
v. Ginkgo Biloba
vi. Melatonin
However, these alternative methods are not strongly supported by scientific studies.
Effective Home Remedies And Suggested Lifestyle Changes To Manage Tinnitus.
In addition to the above-mentioned management techniques that the medical practitioners prescribe, a patient can adopt some simple lifestyle strategies to reduce the stress or irritation associated with tinnitus. They are as follows:
a. Stop fearing the ringing or buzzing that happens in your ears. Know these episodes cannot cause any harm to you.
b. Keep your mind busy with activities that you like to do.
c. Avoid talking about your issue with family and friends.
d. Quit smoking, if you do – smoking narrows the blood vessels that supply vital oxygen to your ears.
e. Try to add some physical activity to your daily routine.
f. Even if your work is getting compromised due to this ringing, do not entirely give up on it. Continue working as much as you can. Of course, don’t let the stress of work mount up.
g. Mobile Apps for sound therapy – The hearing aid manufacturer Resound has developed a sound therapy mobile app that can be used anywhere to mask the sound in your ears. This app gamifies the sound therapy experience by allowing you to play mind relaxing games and design your soundscapes.
While using any of these above-mentioned tinnitus management techniques, it is also essential to prevent it from getting worse at all costs. One of the main reasons behind a worsening condition is noise-induced hearing loss. Therefore tinnitus patients must always be mindful about protecting their ears from exposure to loud noise.
In the next section, we will look at how one can prevent tinnitus from happening.
How To Prevent Tinnitus – All Prevention Techniques
There are many causes of tinnitus that are well within human control. Having knowledge about what causes tinnitus and exercising caution against them can help in preventing this issue. They are covered in detail below:
1. Preventing Ear Infections:
Ear infections can cause tinnitus. If you use earphones or earbuds, or hearing aids, make sure to keep them clean.
Using cotton buds to clean ears is a strict “NO.” If you are worried about excessive earwax building up in your ears, then it’s best to visit an ENT specialist.
2. Reduce Stress and Anxiety:
Tinnitus is closely linked with stress and anxiety. It is advisable to maintain a healthy life balance and include some daily routine habits that help release stress.
3. Reduce Exposure To Loud Noise:
If your work exposes you to loud noises, it is strongly advised to use earplugs to block out the excess sound. Sounds above 85dB are considered to be harmful to the ears. To ensure that you are not exposed to 85dB + sounds, you can use a sound measurement app on your mobile phone.
While in a party or a concert or music festival, stand as far away from the speakers as possible. Even 15 minutes of exposure to the speaker’s loud sound at a close distance can impact your hearing powers forever.
While using headphones or earphones, or earbuds, the golden 60 X 60 rule must always be kept in mind. This means that you should never increase your earphone volume above 60% level and must never continuously use them for over 60 minutes.
Special care must be taken in the case of children.
There is a very insightful video by Dr. Prabha Unadkat that talks about preventing hearing loss. Since tinnitus is directly linked with hearing loss, the same tips can be applied to avert the ringing. You can watch it below.
What Are Researchers Around The Globe Working On To Better Understand, Prevent and Cure Tinnitus?
Inside the complex machinery that powers our hearing mechanism, there are many places where something can go wrong, giving rise to the disruptive ringing and buzzing in your ears. Scientists and medical researchers are particularly interested in learning more about the brain chemistry that gives rise to this issue. A better understanding of that can be used to prevent this problem or possibly even cure it completely.
National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (NIDCD) organized a workshop in 2009 that brought together the best minds from across the globe who are researching on this subject. Below are some of the promising research directions that were picked up from the workshop:
1. Electrical Or Magnetic Stimulation:
Under this method, medical scientists are trying to invent implantable devices that can be used to normalize the neural circuits involved in tinnitus.
2. Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (RTMS):
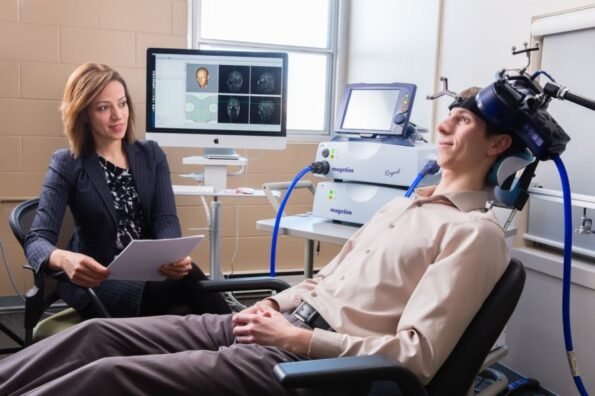
Under the RTMS technique, a small device is placed on the scalp that generates short magnetic pulses. It helps in finding the spots inside the brain that can be stimulated to curb the ringing.
3. Hyperactivity And Deep Brain Stimulation:
Loud noise leads to hyperactivity in the brain. Learning more about this hyperactivity’s nature helps medical researchers develop deep brain stimulations to calm auditory nerves and suppress tinnitus.
4. Resetting The Tonotopic Map

The tonotopic map shows the organizations of neurons in the auditory cortex as per the frequency of the sound to which they respond. The tonotopic map changes on exposing the ears to a loud sound. The medical researchers are trying to learn more about the nature of these changes to possibly develop a technique to bring the tonotopic map of a tinnitus patient back to normal.
With some of the best scientific brains across the world working on solving the mysteries of tinnitus, we can rest assured that future treatments will get better and better. Some strategies for permanent reversal or a cure might also just be around the corner.
We will continue to update this article to keep you informed about the latest developments in this space. So make sure to subscribe to our blogs and follow us on youtube for all the latest updates.
If you are dealing with tinnitus or someone in your family, we hope you found this article helpful. If you have any questions, please feel free to post them in the comments below.
Hear well, Live well.
Related Post
-
 Hearing Loss: Types, Symptoms, Causes & Treatment
Hearing Loss: Types, Symptoms, Causes & Treatment -
 Age-Related Hearing Loss (Presbycusis)
Age-Related Hearing Loss (Presbycusis) -
 How to Safely and Properly Clean Your Ears- Methods & What to Avoid
How to Safely and Properly Clean Your Ears- Methods & What to Avoid -
 Hearing Aids- Benefits, Different Styles/Types and How They Work
Hearing Aids- Benefits, Different Styles/Types and How They Work -
 What Level Of Hearing Loss Requires A Hearing Aid?
What Level Of Hearing Loss Requires A Hearing Aid? -
 Differences Between Conductive and Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Differences Between Conductive and Sensorineural Hearing Loss -
 When is the correct time to upgrade Hearing Aids?
When is the correct time to upgrade Hearing Aids? -
 How Can Hearing Aids Assist School Aged Children?
How Can Hearing Aids Assist School Aged Children? -
 The Impact of Hearing Loss on Cognition
The Impact of Hearing Loss on Cognition -
 Hearing Resides in Your Brain, Not Just Your Ears
Hearing Resides in Your Brain, Not Just Your Ears -
 Exploring Link Between Hearing Loss and Depression_ Breaking the Silence
Exploring Link Between Hearing Loss and Depression_ Breaking the Silence -
 New Hearing Aids? Here’s How To Make The Most Of The Device
New Hearing Aids? Here’s How To Make The Most Of The Device -
 The Unseen Link Between Diabetes and Hearing Loss
The Unseen Link Between Diabetes and Hearing Loss -
 Prevention of Noise-Induced Hearing Loss In Young Adults
Prevention of Noise-Induced Hearing Loss In Young Adults -
 Embarking on the Search for the Right Hearing Aid
Embarking on the Search for the Right Hearing Aid