Differences Between Conductive and Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Table of Contents
What are the Differences Between Conductive and Sensorineural Hearing Loss?

Hearing loss is one of the most prevalent issues that can drastically affect daily life, communication, and quality of life. Understanding the difference between conductive and sensorineural hearing loss is crucial for proper diagnosis as well as treatment. Let’s understand what is sensorineural hearing loss and conductive hearing loss and explore how these two types of hearing loss differ.
Types of Hearing Loss
Hearing loss can be broadly categorized into three primary types:
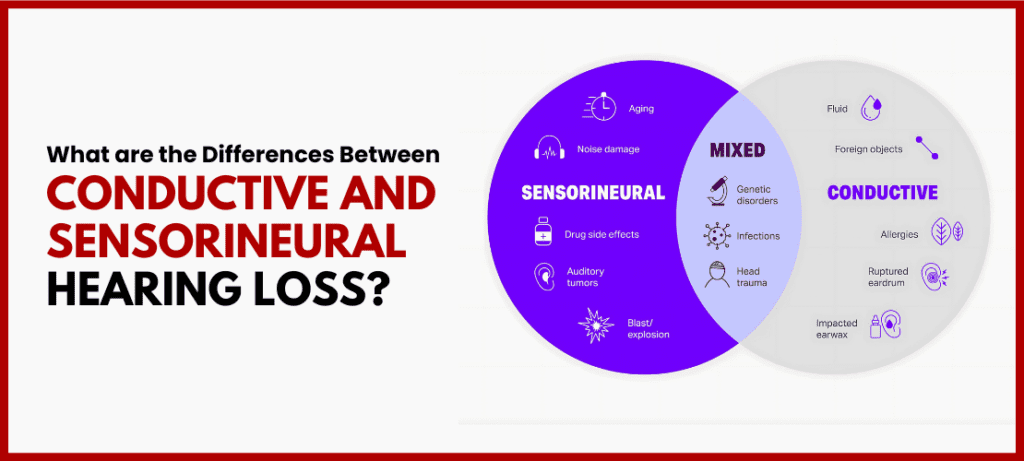
1. Sensorineural Hearing Loss: This kind of hearing loss arises from either the inner ear, known as the cochlea or the nerve pathways to the brain. This is the most common type of hearing loss. This type of hearing loss, also known as Unilateral Sensorineural Hearing Loss, affects one ear and is estimated to impact approximately 7.9-13.3% of the Indian population.
2. Conductive Hearing Loss: In this condition, the outer or middle ear has some form of blockage in the pathway or is damaged, thus creating an impediment that restricts the entry of the sound wave into the inner ear.
3. Mixed Hearing Loss: As the name suggests, this type of hearing loss is a mixed form of sensorineural and conductive hearing loss. The damage occurs simultaneously in the inner ear and the outer or middle ear.
Now that you have an idea about different types of hearing loss let’s understand conductive vs sensorineural hearing loss.
What is Sensorineural Hearing Loss?
Sensorineural hearing loss is associated with damage to the small hair cells in the cochlea (inner ear) or the actual auditory nerve itself, leading to impaired sound-related hearing ability. Although SNHL is typically irreversible, some studies have indicated that hearing may improve with timely treatment or therapy in some instances.
Causes of SNHL
Sensorineural hearing loss causes may include:
- Age-related (presbycusis): Normal, healthy aging damages the hair cells inside your ear and can lead to sensorineural hearing loss.
- Noise exposure: Another common cause of sensorineural hearing loss is damage to inner ear structures caused by prolonged exposure to loud noises.
- Ototoxic medications: Certain drugs, including chemotherapy medications, can damage the inner ear.
- Genetic causes: Congenital conditions (a condition or trait present at birth) affect the inner ear's functioning.
- Infections: Viral infections like mumps or measles may damage the inner ear.
- Head trauma: Traumatic injuries to the inner ear or the auditory nerve.
Symptoms of SNHL
Some of the common sensorineural hearing loss symptoms may include:
- Difficulty hearing in a noisy setting
- Sounds are muffled or distorted
- Trouble discriminating speech, especially consonants
- Tinnitus or ringing in the ears
- Unilateral or bilateral loss of hearing
Impact of SNHL
The impact of SNHL varies from mild inability to distinguish between sounds, even at close distances, to significant loss of hearing that disrupts regular communication.
Types of Sensorineural Hearing Loss
There are various types of sensorineural hearing loss, such as:
- Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss: A common symptom of this SNHL is sudden hearing loss in one or both ears.
- Congenital Sensorineural Hearing Loss: This type of sensorineural hearing loss is typically present at birth. It mainly develops due to genetic factors, developmental issues, gestation (pregnancy) related problems, or other complications during prenatal development or shortly after birth.
- Acquired Sensorineural Hearing Loss: This is the gradual development of hearing loss in later life, either due to age-related factors, illnesses, environmental factors like noise, or neurological conditions like acoustic neuroma.
Diagnosis of SNHL
A comprehensive hearing assessment by an audiologist can identify the degree and type of loss. Some standard techniques include pure tone audiometry, speech tests, and bone conduction tests.
Treatment of SNHL
Sensorineural hearing loss treatment procedure is symptomatic, which means it is focused on controlling symptoms rather than curing the root cause.
- Hearing aids. In individuals with mild to moderate SNHL, perception of sound will be enhanced with hearing aids.
- Cochlear implants. In severe cases, a cochlear implant circumvents damaged sections of the inner ear and stimulates the auditory nerve directly.
- Medications: Medical treatment is possible only in case of sudden sensorineural hearing loss within 2/3 weeks, or healthcare providers may recommend surgical intervention for neurological causes.
- Therapies: Auditory rehabilitation, along with speech therapy, can further improve communication ability.
What is Conductive Hearing Loss?
Conductive hearing loss is a condition where an appropriate amount of sound waves are obstructed from passing through the outer and middle ear and reaching the inner ear. It is more common in children and older adults due to factors like ear infections. Compared to sensorineural hearing loss, conductive hearing loss is typically treatable or even curable, depending on the underlying cause.
Causes of Conductive Hearing Loss
Conductive hearing loss causes may include:
- Ear infections: The most common cause of conductive hearing loss is inflammation or fluid buildup that can disturb sound transmission.
- Earwax buildup: Too much wax can block the ear canal and prevent the sound waves from reaching the inner layer.
- Otosclerosis: The abnormal growth of bones inside the middle ear disturbs the sound wave.
- Perforated eardrum: A perforated (with holes or tears) eardrum can disturb the movement of sound through the ear.
Symptoms of Conductive Hearing Loss
Some of the most common conductive hearing loss symptoms are as follows:
- Inability to hear soft sounds
- The feeling of a plugged ear
- Muffled hearing
- Discomfort or pain in the ear
- Sensitivity to your own voice (autophony)
Impact of Conductive Hearing Loss
Conductive hearing loss can make it difficult to hear faint sounds and impact communication ability and social interactions. If not addressed during the learning stage, it can also impact speech development in children.
Types of Conductive Hearing Loss
The types of conductive hearing loss are as follows:
1. Acute Conductive Hearing Loss: This type of conductive hearing loss is usually associated with infections or sudden obstructions, which are usually easily treatable.
2. Chronic Conductive Hearing Loss: Persistent problems arising from long-term diseases, such as otosclerosis (abnormal bone growth in the middle ear) or chronic infections, cause hearing difficulties.
Diagnosis of Conductive Hearing Loss
An audiologist may perform otoscopy, tympanometry, and audiometric testing to establish the cause and extent of conductive hearing loss.
Conductive Hearing Loss Treatment
Conductive hearing loss treatment procedure depends on the cause:
- Medical treatment: Antibiotics or ear drops for an infection.
- Surgical treatment: Surgery such as mastoidectomy or tympanoplasty to treat a perforated (torn) eardrum or to remove blockages.
- Hearing aids: Healthcare providers recommend these in cases where medical treatments or surgical interventions will not work.
Conductive Hearing Loss vs Sensorineural Hearing Loss – A Glance at the Differences
Let’s take a quick look at conductive hearing loss vs sensorineural hearing loss:
| Factor | Conductive Hearing Loss | Sensorineural Hearing Loss |
|---|---|---|
| Affected Area | Outer or middle ear | Inner ear (cochlea) or auditory nerve |
| Causes | Infections, earwax, perforated eardr | Aging, noise exposure, genetic factors |
| Treatment Options | Medical or surgical interventions | Medical or surgical interventions |
| Reversibility | Often reversible with treatment | Usually permanent |
| Sound Perception | Muffled or blocked | Distorted or unclear |
How to Tell if Hearing Loss is Sensorineural or Conductive
Understanding the difference between conductive and sensorineural hearing loss
requires a thorough examination by an audiologist. The audiologist studies the patient’s details elaborately before finalizing a diagnosis. Pure tone audiometry and tympanometry would guide appropriate treatment by determining the nature and location of the problem.
A Note on Preventing Hearing Loss by Dr. Prabha
It is always better than cure & hearing loss can easily be prevented. Here are a few tips to help protect your hearing:
- Avoid activities that involve loud noise.
- Monitor the volume of your devices. The rule is to use 60% of the volume, at most 80 dba.
- Some medicines can affect your hearing, for example: Antibiotics Diuretics or Chemotherapy drugs.
- Manage Health Conditions like diabetes and hypertension, which are likely to cause neurovascular diseases.
- Avoid using foreign objects and non-medical treatment to clean your ears.
- Maintain good ear hygiene
- Early diagnosis and interventions can reduce the impact of hearing loss.
How Quality Hearing Care Can Help
At Quality Hearing Care, we offer customized diagnostic assessments for both sensorineural and conductive hearing loss. Our experienced team will help you through the diagnostic process and provide advanced hearing aid technology to help you reconnect with the sounds that matter. Contact us now to schedule an appointment.
FAQs
No, conductive hearing loss is typically transitory and treatable with medical or surgical interventions based on what is causing it.
Sensorineural hearing loss can worsen based on whether it is caused by aging or constant exposure to noise. Early intervention is essential to ensure positive outcomes.
Sensorineural hearing loss treatment options include hearing aids, cochlear implants, and medication such as corticosteroids. This depends on the degree and cause.
Modern treatments have shown that, although sensorineural hearing loss is generally permanent, good hearing can be restored considerably through techniques like cochlear implants and advanced hearing aids.
Related Post
-
 Hearing Loss: Types, Symptoms, Causes & Treatment
Hearing Loss: Types, Symptoms, Causes & Treatment -
 Age-Related Hearing Loss (Presbycusis)
Age-Related Hearing Loss (Presbycusis) -
 How to Safely and Properly Clean Your Ears- Methods & What to Avoid
How to Safely and Properly Clean Your Ears- Methods & What to Avoid -
 Hearing Aids- Benefits, Different Styles/Types and How They Work
Hearing Aids- Benefits, Different Styles/Types and How They Work -
 What Level Of Hearing Loss Requires A Hearing Aid?
What Level Of Hearing Loss Requires A Hearing Aid? -
 Differences Between Conductive and Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Differences Between Conductive and Sensorineural Hearing Loss -
 When is the correct time to upgrade Hearing Aids?
When is the correct time to upgrade Hearing Aids? -
 How Can Hearing Aids Assist School Aged Children?
How Can Hearing Aids Assist School Aged Children? -
 The Impact of Hearing Loss on Cognition
The Impact of Hearing Loss on Cognition -
 Hearing Resides in Your Brain, Not Just Your Ears
Hearing Resides in Your Brain, Not Just Your Ears -
 Exploring Link Between Hearing Loss and Depression_ Breaking the Silence
Exploring Link Between Hearing Loss and Depression_ Breaking the Silence -
 New Hearing Aids? Here’s How To Make The Most Of The Device
New Hearing Aids? Here’s How To Make The Most Of The Device -
 The Unseen Link Between Diabetes and Hearing Loss
The Unseen Link Between Diabetes and Hearing Loss -
 Prevention of Noise-Induced Hearing Loss In Young Adults
Prevention of Noise-Induced Hearing Loss In Young Adults -
 Embarking on the Search for the Right Hearing Aid
Embarking on the Search for the Right Hearing Aid
